Static IP Configuration
Purposes and Advantages of Static IP
Static IP configuration ensures that a device maintains a fixed address on the network, providing stable and reliable network connectivity for various application scenarios.
Main Application Scenarios
-
Ensuring Device Accessibility
- Devices always maintain the same IP address, making remote access and control easier
- Suitable for scenarios requiring fixed addresses, such as web servers, MQTT communication, PLC control, etc.
-
Simplifying Network Management
- Fixed IPs are required for devices such as cameras, sensors, and controllers in LAN or industrial networks
- Facilitates stable connections for other systems and services
-
Adapting to Special Network Environments
- Static IP must be used in environments without DHCP service (e.g., industrial control, edge computing)
- Avoids reliance on dynamic address allocation
-
Improving Development and Debugging Efficiency
- Fixed IP addresses make it easier to locate and connect to devices quickly
- Simplifies repetitive testing processes
-
Supporting Device Discovery Mechanisms
- Static IP ensures devices respond as expected when accessing predefined IP ranges
Comparison of Static IP Advantages
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| ✅ Stable and Reliable | The IP address remains unchanged, ensuring stable communication for long-running devices |
| ✅ Friendly for Headless Environments | Suitable for use in embedded devices without a graphical interface |
| ✅ Convenient for Remote Maintenance | More efficient when connecting via SSH, Web, API, etc. |
| ✅ Adaptable to Closed Networks | Static IP is required in industrial networks or private networks without DHCP |
| ✅ Supports Automation | Deployment, monitoring, and update scripts rely on consistent IP addresses to run |
System-side Configuration
- Avoid using IP addresses close to boundary values such as
0,1,254,255 - Using
192.168.1.254may result in conflicts with other applications, causing unstable connections - It is recommended to use IP addresses in the middle range, such as
192.168.1.100-192.168.1.200
Configuration Steps
-
Connect to the System Terminal
- Use SSH to connect to the device
-
Check Network Interfaces
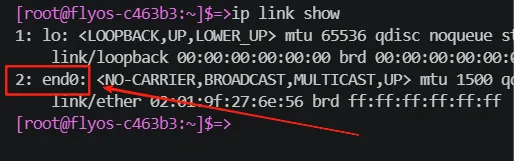
- Run the command:
ip link show - Record the network interface name, such as
eth0,end0
- Run the command:
-
Edit the Network Configuration File
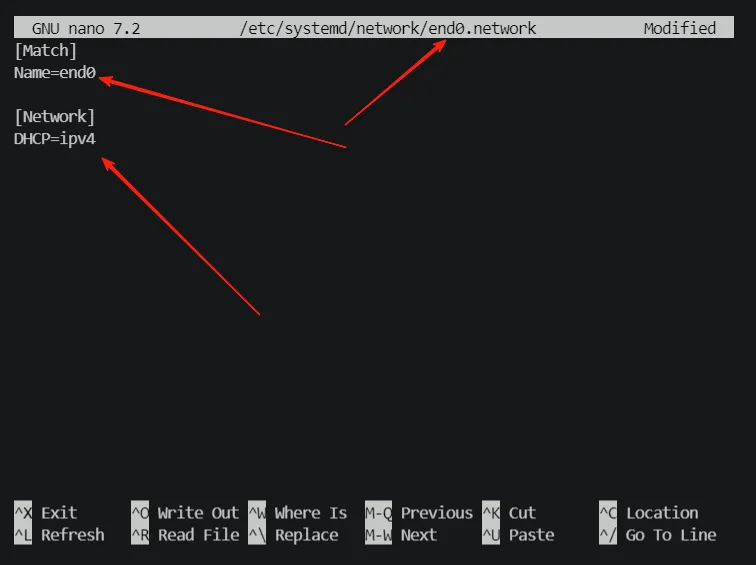
- Run the command:
nano /etc/systemd/network/end0.network - Note: Replace
end0in the filename with the actual network interface name
- Run the command:
-
Configure Static IP Parameters
- Modify the file content as follows (adjust according to the actual network environment):
[Match]
# Match the network interface name; modify as needed
Name=end0
[Network]
# Set the static IP address and subnet mask
# /24 indicates a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0
Address=192.168.1.100/24
# Set the default gateway address
Gateway=192.168.1.1
# Set the DNS servers
DNS=8.8.8.8
DNS=114.114.114.114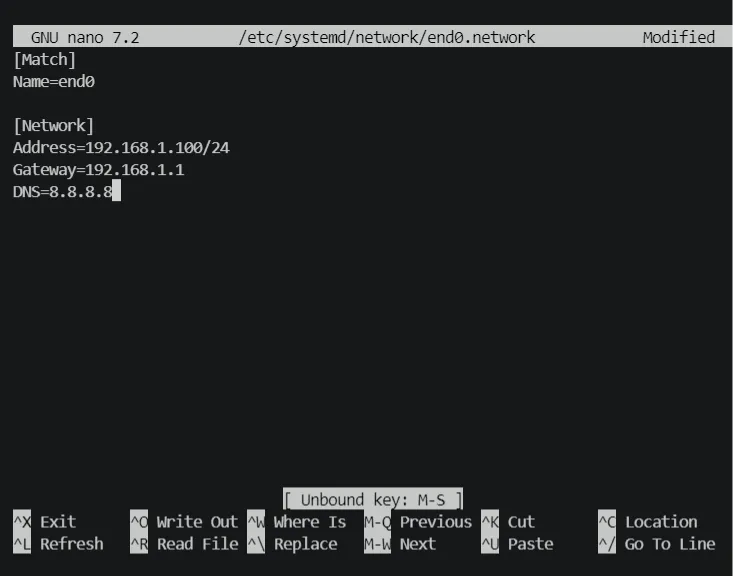
-
Save and Apply the Configuration
- Press
Ctrl + Sto save the file - Press
Ctrl + Xto exit the editor - Restart the network service with the command:
systemctl restart systemd-networkd
- Press
-
Verify the Configuration
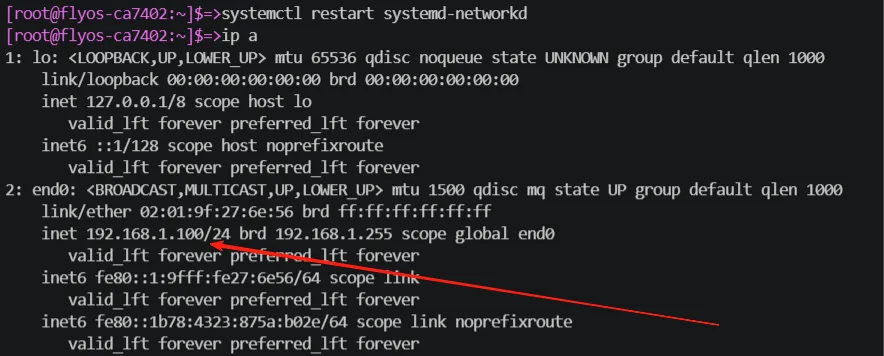
- Run the command:
ip a - Confirm that the displayed IP address matches the configured one
- Run the command:
PC-side Configuration
To ensure the PC can communicate properly with devices configured with static IPs, corresponding network configurations must be made on the PC.
Network Parameter Settings
| Parameter | Configuration Requirements | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Local IP | 192.168.1.xxx | Must be in the same subnet as the device IP |
| Gateway | 192.168.1.1 | Must match the gateway set on the device |
| Subnet Mask | 255.255.255.0 | Corresponds to the /24 configuration of the device IP |
| DNS Server | 8.8.8.8, 114.114.114.114 | Use common public DNS services |
Configuration Methods
Windows System
- Open "Network and Sharing Center"
- Click "Change adapter settings"
- Right-click the currently used network connection and select "Properties"
- Double-click "Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)"
- Select "Use the following IP address" and fill in the corresponding parameters
macOS System
- Open "System Preferences" → "Network"
- Select the currently used network connection
- Click "Advanced" → "TCP/IP"
- Set "IPv4" to "Manual"
- Fill in the corresponding IP address, subnet mask, and router address
Connectivity Test
After configuration, it is recommended to perform a connectivity test:
# Run the ping command on the PC to test connectivity
ping 192.168.1.100
# If replies are received, the network configuration is successful
If the device cannot be pinged, please check:
- Whether the network cable is properly connected
- Whether the firewall is blocking communication
- Whether the IP addresses are in the same subnet
- Whether the subnet mask and gateway configuration are correct